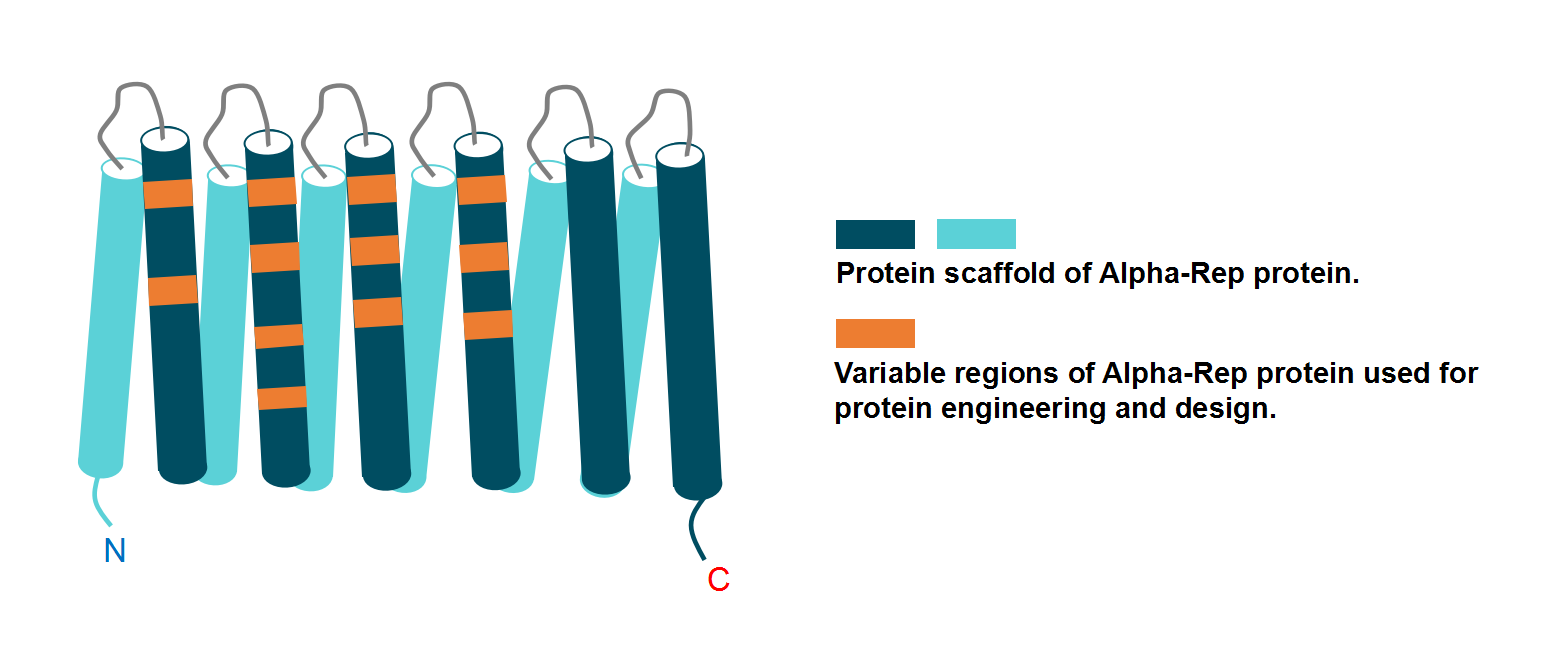
| 1 |
The Rep artificial repeat protein scaffold: a new tool for crystallization and live cell applications. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Oct;43(5):819-24.
|
| 2 |
Structural and functional analysis of the fibronectin-binding protein FNE from Streptococcus equi spp. equi. FEBS J. 2014 Dec;281(24):5513-31.
|
| 3 |
Selection and Characterization of Artificial Proteins Targeting the Tubulin Subunit. Structure. 2019 Mar 5;27(3):497-506.e4.
|
| 4 |
Selection of specific protein binders for pre-defined targets from an optimized library of artificial helicoidal repeat proteins (alphaRep). PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e71512.
|
| 5 |
Ligand-induced conformational switch in an artificial bidomain protein scaffold. Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 4;9(1):1178.
|
| 6 |
alphaRep A3: A Versatile Artificial Scaffold for Metalloenzyme Design. Chemistry. 2017 Jul 26;23(42):10156-10166.
|
| 7 |
Specific GFP-binding artificial proteins (Rep): a new tool for in vitro to live cell applications. Biosci Rep. 2015 Jun 12;35(4):e00223.
|
| 8 |
Alpha repeat proteins (Rep) as expression and crystallization helpers. J Struct Biol. 2018 Feb;201(2):88-99.
|
| 9 |
Occupation of a thermoresistant-scaffold (Rep) at SP1-NC cleavage site disturbs the function of HIV-1 protease. Biosci Rep. 2020 Jun 26;40(6):BSR20201131.
|
| 10 |
Insight into microtubule nucleation from tubulin-capping proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 14;116(20):9859-9864.
|